T0. math
My idea :
Let f(n)=x^n+x^{-n} . Notice that f(1)=k
And when 2 \mid n , f^2(\frac{n}{2}) = (x^{\frac{n}{2}}+x^{-\frac{n}{2}})^2=x^n+x^{-n}+2x^{\frac{n}{2}}x^{-\frac{n}{2}} = f(n)+2 .
Therefore, 2 \mid n , f(n) = f^2(\frac{n}{2})-2 .
Based on this formula, we can get f(n) withb a complexity of O(\log_2 n) .
Bug :
When 2 \nmid n , f^2(\frac{n-1}{2}) = f(n-1)-2 .
Now we need to solve f(n-1) .
But, currently, I found this formula : f(n-1)f(1) = (x^{n-1}+x^{-n+1})(x+x^{-1}) = x^n + x^{-n} + x^{n-2} + x^{-n+2} = f(n) + f(n-2) .
Therefore, f(n) = f(n-1)f(1)-f(n-2) .
If we directly use above idea to solve it, the complexity will be O(n) , TLE.
(Right) idea :
Actually, we are colse enough to the answer.
Notice that f(1) is a given constant k .
So the equation will be f(n) = kf(n-1)-f(n-2) .
Seems familiar?
When we meet such formula… we can use matrix!
T0-EX. Matrix qkp Extension
Did you still remember this passage ?
There, we show the example of solving fibonacci numbers with matrix.
In fact, it can be used in such problems.
Thing about the form of the matrix :
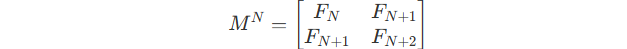
And how we get M^{N+1} :
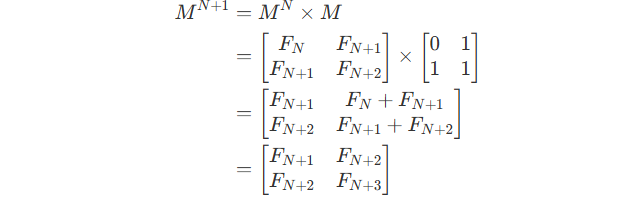
Here, we designed a matrix M so that it satisfies those properties above.
However, the generalize this method, we face 2 problems :
- Sometimes the initial condition not equals to M.
- Sometimes the coefficient changes, maybe (2, 3), (5, 8), (114514, 191981).
For the first problem, just change the formula : M^N into M_0 \times M^N .
Here, M_0 is the initial status of the sequence, M shows the relations between these terms in the sequence.
For the second problem, go back to the equation.
Suppose that we have a sequence that satisfies $AN = pA{N-1} + qA_{N-2}$ .
And we have calculated
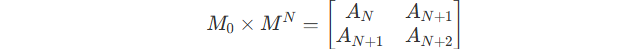
Now we expected to get M_0 \times M^{N+1} by calculating :
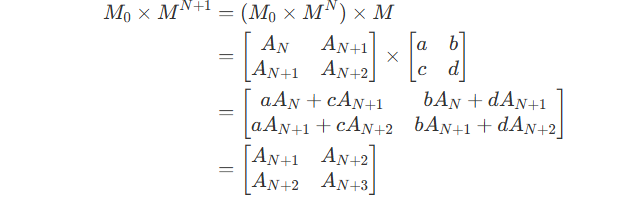
By comparing the terms, we can get :
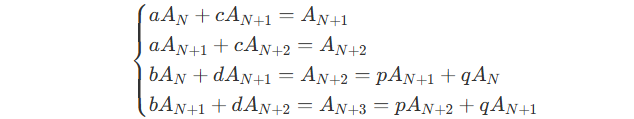
By comparing the coefficients, we can get :
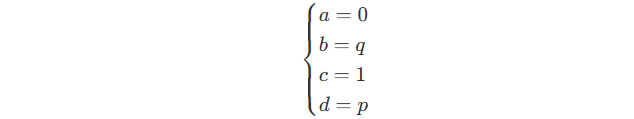
So the matrix M is :
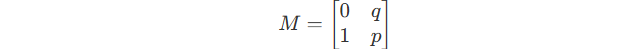
To initialize, the matrix M_0 should be :
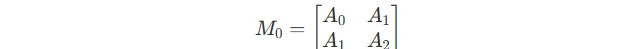
So, based on M_0 and M , we can solve the sequence quickly!
T0. math (Part II)
If you read the prev. page carefully, you must know how to use the conclusion.
Go back to the formula f(n) = kf(n-1)-f(n-2) .
If we consider f(n) as an element of a sequence, just set p=k, q=-1 , we can solve f(n) by matrix qkp.
Code :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<long long> V1D;
typedef vector<V1D> V2D;
class Matrix {
private:
V2D value;
long long MH, MW;
public :
// Matrix() {}
Matrix(V2D Vec) {value=Vec;MH=Vec.size(), MW=Vec[0].size();}
Matrix(long long H, long long W) {
MH=H, MW=W;
for (long long i=0;i<H;i++) value.push_back(V1D(W));
}
long long getHeight() {return MH;}
long long getWidth() {return MW;}
long long getValue(long long y, long long x) {return value[y][x];}
void change(long long y, long long x, long long v) {value[y][x] = v;}
V2D matrixVec() {return value;}
Matrix operator+(Matrix Mx) {
long long Hx=Mx.getHeight(), Wx=Mx.getWidth();
if (Hx != MH || Wx != MW) {
cout << "Matrix Exception (operator+, E1) : Size not equal.";
exit(0);
}
Matrix Mr(MH, MW);
for (long long i=0;i<MH;i++) {
for (long long j=0;j<MW;j++) Mr.change(i, j, value[i][j]+Mx.getValue(i, j));
}
return Mr;
}
Matrix operator-(Matrix Mx) {
long long Hx=Mx.getHeight(), Wx=Mx.getWidth();
if (Hx != MH || Wx != MW) {
cout << "Matrix Exception (operator-, E2) : Size not equal.";
exit(0);
}
Matrix Mr(MH, MW);
for (long long i=0;i<MH;i++) {
for (long long j=0;j<MW;j++) Mr.change(i, j, value[i][j]-Mx.getValue(i, j));
}
return Mr;
}
Matrix operator*(Matrix Mx) {
long long Hx=Mx.getHeight(), Wx=Mx.getWidth();
if (MW!=Hx) {
cout << "Matrix Exception (operator*, E3) : Illegal H/W.";
exit(0);
}
Matrix Mr(MH, Wx);
for (long long i=0;i<MH;i++) {
for (long long j=0;j<Wx;j++) {
long long cur=0;
for (long long k=0;k<MW;k++) cur += value[i][k] * Mx.getValue(k, j);
Mr.change(i, j, cur);
}
}
return Mr;
}
Matrix operator%(long long MOD) {
Matrix Mr(value);
for (long long i=0;i<MH;i++) {
for (long long j=0;j<MW;j++) Mr.change(i, j, Mr.getValue(i, j)%MOD);
}
return Mr;
}
};
Matrix UnitMatrix(long long K) {
Matrix M0(K, K);
for (long long i=0;i<K;i++) M0.change(i, i, 1);
return M0;
};
Matrix qkMpow(Matrix Mx, long long e, long long MOD) {
long long K = Mx.getHeight();
if (e==0) return UnitMatrix(K);
if (e==1) return Mx;
Matrix HF = qkMpow(Mx, e/2, MOD);
if (e&1) return ((HF*HF)*Mx)%MOD;
return (HF*HF)%MOD;
};
int main() {
long long N, K, MD;cin >> MD >> K >> N;
Matrix M0(2, 2), MP(2, 2);
M0.change(0, 0, 2);
M0.change(0, 1, K);
M0.change(1, 0, K);
M0.change(1, 1, ((K*K)%MD-2+MD)%MD);
MP.change(0, 1, -1);
MP.change(1, 0, 1);
MP.change(1, 1, K);
Matrix Mx = qkMpow(MP, N, MD);
Matrix M = M0*Mx;
V2D Vec = M.matrixVec();
cout << (Vec[0][0]+MD)%MD;
return 0;
}
Note :
Because the coefficient q is negative, when get the result, add it by MD and modulo it again.
This code can correctly answer all samples.
Not all cases!