0. gcdsum
Notice that the target function g(n) satisfies g(n)=g(n-1)+\sum_{i=1}^{n-1} \gcd(i,n)
So, for g(n), if we get the value of g(n-1) and h(n)=\sum_{i=1}^{n-1}{\gcd(i,n)}, we can get g(n) immediately.
Now we need to calculate the value of h(n)
Construct f(n)=h(n)+n=\sum_{i=1}^n{\gcd(i,n)}
Notice that
The function is productive : f(ab)=f(a)f(b)
For a prime : f(p)=2p+1
For the power of a prime : f(p^q)=p^q+q(p-1)^{(q-1)}
Here, p is a prime, and \gcd(a,b)=1
Note
(I can\’t proof statement 1, can you help me?)
Then, for n=\Pi_{i=1}^k{p_i^{q_i}}
Use f(n)=\Pi_{i=1}^kf(p_i^{q_i}) can calculate h(n) faster.
Here p_i are all primes.
Code :
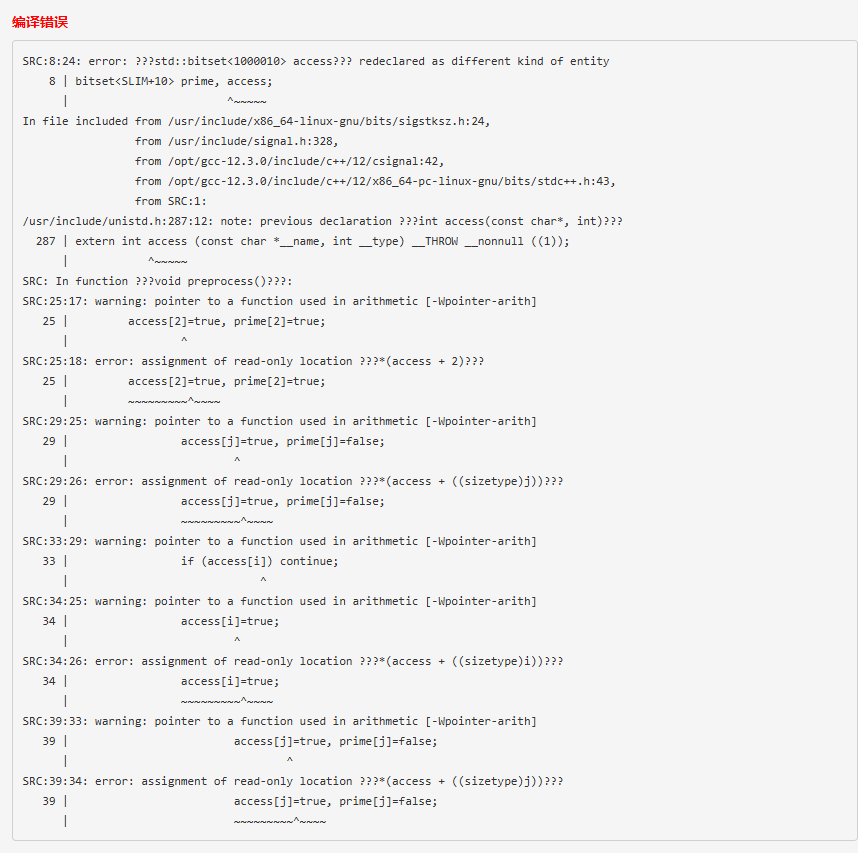
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const long long SLIM=100000;
long long LIM;
long long fsum[SLIM+10], gsum[SLIM+10];
bitset<SLIM+10> prime, vis;
long long lprime[SLIM+10], primelist[80000], primecount;
vector<long long> divs;
map<long long, long long> pfac;
long long i,j,k,pm,pexp;
long long part;
long long qkpow(long long a, long long e) {
if (e==0) return 1;
if (e==1) return a;
long long hf=qkpow(a, e/2);
if (e%2) return hf*hf*a;
return hf*hf;
}
void preprocess() {
// prime sieve
vis[2]=true, prime[2]=true;
primelist[primecount++]=2;
lprime[2]=1;
for (j=4;j<=LIM+10;j+=2) {
vis[j]=true, prime[j]=false;
lprime[j]=1;
}
for (i=3;i<=LIM+10;i++) {
if (vis[i]) continue;
vis[i]=true;
prime[i]=true;
lprime[i]=++primecount;
primelist[primecount-1]=i;
for (j=2*i;j<=LIM+10;j+=i) {
vis[j]=true, prime[j]=false;
lprime[j]=(lprime[j]?lprime[j]:primecount);
}
}
//end
//fsum compute
long long bk;
pfac.clear();
for (i=2;i<=LIM+10;i++) {
if (prime[i]) {
fsum[i]=2*i-1;
continue;
}
bk = i;
pfac.clear();
for (j=primelist[lprime[bk]-1];bk!=1;j=primelist[lprime[bk]-1]) {
if (pfac.find(j)==pfac.end()) pfac[j]=0;
while(!(bk%j)) pfac[j]++, bk/=j;
}
if (pfac.size()==1) {
pm=(*pfac.begin()).first, pexp=(*pfac.begin()).second;
fsum[i]+=qkpow(pm, pexp);
part=qkpow(pm, pexp-1);
fsum[i]+=pexp*(pm-1)*part;
}
else {
divs.clear();
for (map<long long, long long>::iterator it=pfac.begin();it!=pfac.end();it++) {
divs.push_back(qkpow(it->first, it->second));
}
fsum[i]=1;
for (k=0;k<divs.size();k++) fsum[i]*=fsum[divs[k]];
}
}
gsum[1]=0;
for (i=2;i<=LIM+10;i++) gsum[i]=gsum[i-1]+fsum[i]-i;
/*
cout << "{";
for (i=2;i<=LIM+10;i++) printf("%15lld,", gsum[i]);
cout << "}";
exit(0);
*/
}
int main() {
freopen("table1.out", "w", stdout);
long long T;cin >> T;
vector<int> Qs;
for (long long _T=0;_T<T;_T++) {
long long X;cin >> X;
LIM = max(LIM, X);
Qs.push_back(X);
}
preprocess();
for (int i=0;i<T;i++) cout << gsum[Qs[i]] << endl;
return 0;
}
Optimizes :
- Set the limit to the maximum value of queries to reduce pre-process time. (Line 89)
- When finding primes, record each number\’s lowest prime factor (Line 30, 40), and when finding all prime factors of a number, use this info to accelerate (Line 54).
Complexity :
- preprocess : about O(n)
- single query : O(1)
- Real time :
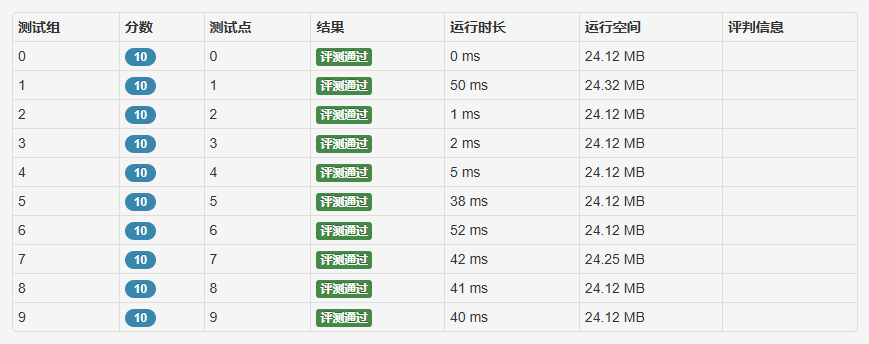
Such a joke :