Extend 3.1 : Disjoint Set
Example :

Figure 6.1 : Disjoint Set
Disjoint Set is a set. It can do merge(), find(), and other
1. find()
You only need to search upwards and upwards, until you find the root.
If a node r is the root of a tree, par[r] = r.
For example, node 5, the parent par[5]=5, so find(5) = 5.
More example will appear after merge().
2. merge()
It is quite easy. Find their roots, and change one’s par[] to another one.
For example, we want to merge node 3 and 4, find root 3, 4, and point4 to 3 or 3 to 4.
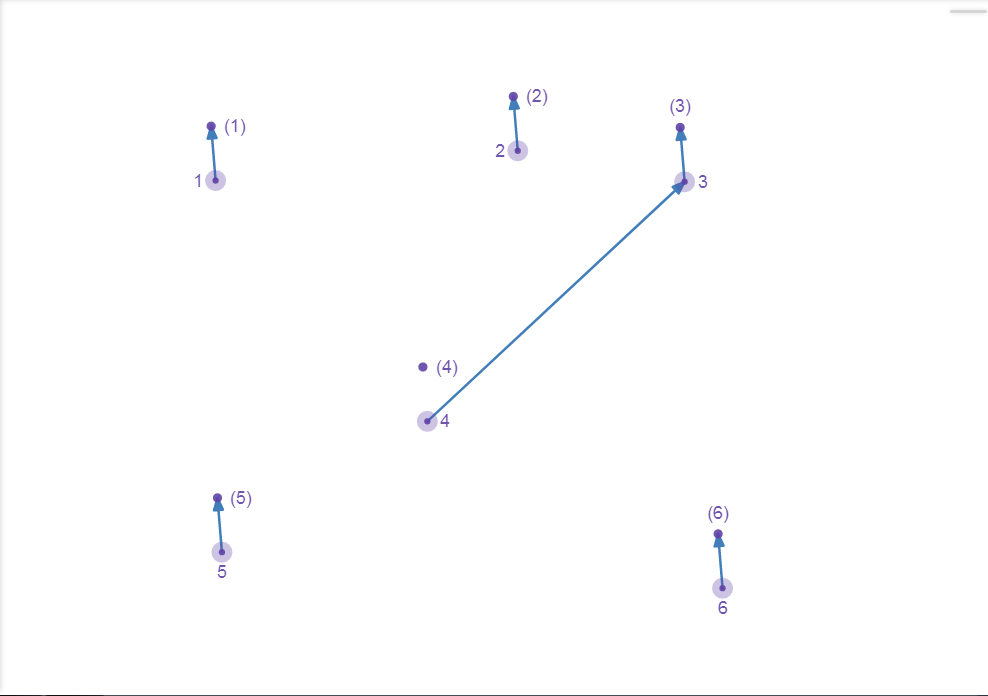
Figure 6.2 : Disjoint Set – merge
Here, I’ll also show you how find() works.
Another Example, we want to find the root of 4.
Step 1, we find its parent, 3.
And next, we find its parent, 3, itself.
So, the root of 4 is 3.
Optimize : merge by rank.
Now, we want to merge node 1 and 3.
We can point 3 to 1 or 1 to 3.
Which one is better?
As is known to us, we should point 1 to 3. Because the depth of 1 is smaller than 3.
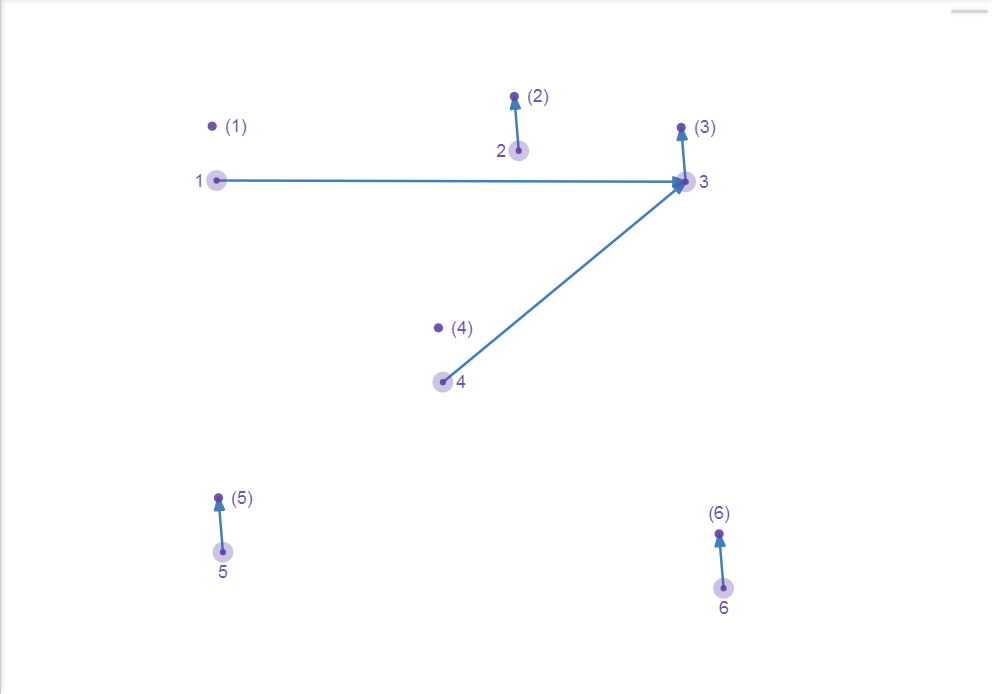
Figure 6.3 : Disjoint Set – Optimized merge
But, how does the program know it?
We defines rank here.
The rank of a node can be regarded to the depth of its sons.
For example the rank of 1 and 5 are both 1.
When we merge the node u and v, if rank[u] <= rank[v], we point u to v.Otherwise, we point v to u.
If rank[u] equals to rank[v], rank[v] should add by 1.
It will make the code more efficienty.
Given Score :
Difficulty : 2
x Basic Score : 36 />
Score : 498
All Figures in the passage :
http://59.60.22.18:2500/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/C03_Figures.zip