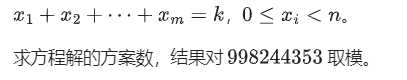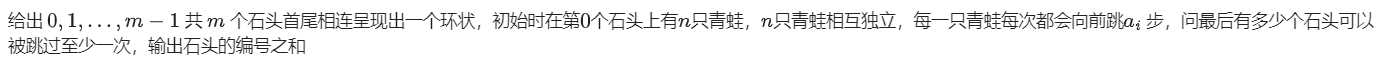T0
刚写完你告诉我又没有了???
T1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const LL N = 6e6 + 5, M = 6e6, mod = 998244353;
LL n, m, k, fact[N], infact[N];
LL quick_power(LL a, LL b) {
LL res = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1)
res = (LL)res * a % mod;
a = (LL)a * (LL)a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
void init() {
fact[0] = infact[0] = 1;
for (LL i = 1; i <= M; i++) {
fact[i] = (LL)fact[i - 1] * i % mod;
infact[i] = (LL)infact[i - 1] * quick_power(i, mod - 2) % mod;
}
}
LL C(LL a, LL b) {
if (a < b || a < 0 || b < 0)
return 0;
else
return (LL)fact[a] * infact[b] % mod * infact[a - b] % mod;
}
void work() {
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &n, &m, &k);
k += m;
k--;
LL res = 0;
for (LL i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
LL t = C(m, i);
t = 1LL * t * C(k - n * i, m - 1) % mod;
if (i % 2)
res = (((res - t) % mod) + mod) % mod;
else
res = (res + t) % mod;
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
int main() {
init();
LL T;
scanf("%lld", &T);
while (T--) work();
return 0;
}
T2
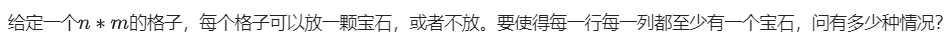
先只考虑单列的情况:
用广义容斥原理,奇加偶减
每一列答案C(m,i)(2^(m-i)-1)^n(-1)^n.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const LL N = 6e6 + 5, M = 6e6, mod = 1e9 + 7;
LL n, m, k, fact[N], infact[N];
LL quick_power(LL a, LL b) {
LL res = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1)
res = (LL)res * a % mod;
a = (LL)a * (LL)a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
void init() {
fact[0] = infact[0] = 1;
for (LL i = 1; i <= M; i++) {
fact[i] = (LL)fact[i - 1] * i % mod;
infact[i] = (LL)infact[i - 1] * quick_power(i, mod - 2) % mod;
}
}
LL C(LL a, LL b) {
if (a < b || a < 0 || b < 0)
return 0;
else
return (LL)fact[a] * infact[b] % mod * infact[a - b] % mod;
}
void work() {
scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m);
LL res = 0;
for (LL i = 0; i <= m; i++) {
LL t = C(m, i) * quick_power((quick_power(2, m - i) - 1), n) % mod * quick_power(-1, i) % mod;
res = ((res + t) % mod + mod) % mod;
}
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
int main() {
init();
work();
return 0;
}
T3
LUOGU
先考虑完全背包问题,但是并没有限制。
于是考虑只对一个硬币限制的情况,答案是dp[S-c[i]*(d[i]+1)]
那么对于4个硬币的限制,我们就逐一把4个硬币单独限制的方案数减掉,再把4个硬币两两同时限制的方案数加上,再把4个硬币三三同时限制减掉,最后加上4个同时限制的方案数就是我们所需的答案。
不难发现,这不就是容斥原理.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
typedef long long LL;
int n;
LL s, c[10], d[10], f[N];
LL get(int x) { return c[x] * (d[x] + 1); }
void work() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) scanf("%lld", &d[i]);
scanf("%lld", &s);
LL res = f[s];
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
if (s - get(i) >= 0)
res -= f[s - get(i)];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= 4; j++) {
if (s - get(i) - get(j) >= 0)
res += f[s - get(i) - get(j)];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= 4; j++) {
for (int k = j + 1; k <= 4; k++) {
if (s - get(i) - get(j) - get(k) >= 0)
res -= f[s - get(i) - get(j) - get(k)];
}
}
}
if (s - get(1) - get(2) - get(3) - get(4) >= 0)
res += f[s - get(1) - get(2) - get(3) - get(4)];
printf("%lld\n", res);
}
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) scanf("%lld", &c[i]);
f[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
for (int j = c[i]; j < N; j++) f[j] += f[j - c[i]];
}
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n--) work();
return 0;
}
T4
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
typedef long long LL;
int n;
LL m, a[N], st[N];
vector<int> d;
LL get(LL a, LL b) { return a * b + b * (b - 1) / 2 * a; }
void init() {
d.clear();
for (LL i = 1; i <= m / i; i++) {
if (!(m % i)) {
d.push_back(i);
if (i != m / i)
d.push_back(m / i);
}
}
sort(d.begin(), d.end());
}
void work(int T) {
scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m);
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
for (LL i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%lld", &a[i]);
a[i] = __gcd(a[i], m);
}
init();
for (LL i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (LL j = 0; j < d.size(); j++) {
if (!(d[j] % a[i]))
st[j] = 1;
}
}
LL res = 0;
for (LL i = 0; i < d.size(); i++) {
res += st[i] * get(d[i], (m - 1) / d[i]);
for (int j = i + 1; j < d.size(); j++) {
if (!(d[j] % d[i]))
st[j] -= st[i];
}
}
printf("Case #%d: %lld\n", T, res);
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
for (int i = 1; i <= T; i++) work(i);
return 0;
}
T5
LUOGU
状压DP.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const LL N = 25, mod = 1000000007;
LL n, S, c[N][N], f[1 << N], dp[1 << N];
LL lowbit(LL x) { return x & (-x); }
int main() {
scanf("%lld", &n);
S = (1 << n) - 1;
for (LL i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (LL j = 1; j <= n; j++) scanf("%lld", &c[i][j]);
}
for (LL k = 0; k <= S; k++) {
f[k] = 1;
for (LL i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (k & (1 << i - 1)) {
for (LL j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (k & (1 << j - 1))
f[k] = f[k] * (c[i][j] + 1) % mod;
}
}
}
}
for (LL k = 1; k <= S; k++) {
dp[k] = f[k];
LL p = k ^ lowbit(k);
for (LL i = p; i; i = (i - 1) & p) dp[k] = ((dp[k] - (f[i] * dp[i ^ k]) % mod) + mod) % mod;
}
printf("%lld", dp[S]);
return 0;
}
T6

很显然,这是一个DP计数+容斥。
但是我们发现,直接DP会超时,采用树状数组优化。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2005;
const LL mod = (LL)(1e9 + 7);
int n;
LL a[N], f[N], g[N], tr[N], fac[N];
vector<LL> V;
int lowbit(int x) { return x & (-x); }
void modify(int x, LL v) {
for (; x <= V.size(); x += lowbit(x)) tr[x] = (tr[x] + v) % mod;
}
LL query(int x) {
LL res = 0;
for (; x; x -= lowbit(x)) res = (res + tr[x]) % mod;
return res;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
V.push_back(a[i]);
}
sort(V.begin(), V.end());
V.erase(unique(V.begin(), V.end()), V.end());
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = lower_bound(V.begin(), V.end(), a[i]) - V.begin() + 1;
g[i] = 1;
}
f[1] = n;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
LL ans = 0;
memset(tr, 0, sizeof tr);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
modify(a[j], g[j]);
if (j >= i)
g[j] = ((query(a[j]) - g[j]) % mod + mod) % mod;
else
g[j] = 0;
ans = (ans + g[j]) % mod;
}
f[i] = ans;
}
fac[1] = 1;
LL res = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * (LL)i % mod;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
res = (res + (f[i] * fac[n - i] % mod - f[i + 1] * fac[n - i - 1] % mod * (i + 1) % mod) + mod) % mod;
printf("%lld", res);
return 0;
}
T7
ACWING
莫比乌斯函数+容斥+二分
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n, primes[N], mu[N], st[N], cnt;
void init() {
mu[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
if (!st[i]) {
primes[cnt++] = i;
mu[i] = -1;
}
for (int j = 0; primes[j] * i < N; j++) {
st[primes[j] * i] = 1;
if (i % primes[j] == 0)
break;
mu[primes[j] * i] = -mu[i];
}
}
}
LL get(LL x) {
LL s = 0;
for (LL i = 1; i <= x / i; i++) s += 1LL * mu[i] * (LL)(x / (i * i));
return s;
}
void work() {
LL k;
scanf("%lld", &k);
LL l = 1, r = 1e10;
while (l < r) {
LL mid = l + r >> 1;
if (get(mid) >= k)
r = mid;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
printf("%lld\n", l);
}
int main() {
init();
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) work();
return 0;
}
T8
ACWING
预处理欧拉函数前缀和,用整除分块。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 500005;
int n, m, primes[N], mu[N], st[N], cnt;
LL s[N], res = 0;
void init() {
mu[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
if (!st[i]) {
primes[cnt++] = i;
mu[i] = -1;
}
for (int j = 0; primes[j] * i < N; j++) {
st[primes[j] * i] = 1;
if (i % primes[j] == 0)
break;
mu[primes[j] * i] = -mu[i];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) s[i] = s[i - 1] + (LL)mu[i];
}
int main() {
init();
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int d = 1; d <= n; d++) {
int k = min(n, m) / d;
LL ans = 0;
for (int l = 1, r; l <= k; l = r + 1) {
r = min(n / (n / l), m / (m / l));
ans += 1LL * (s[r] - s[l - 1]) * (n / (d * l)) * (m / (d * l));
}
res += 1LL * d * ans;
}
printf("%lld", (res << 1) - 1LL * n * m);
return 0;
}
T9
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 50005;
int primes[N], mu[N], s[N], st[N], cnt;
void init() {
mu[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
if (!st[i]) {
primes[cnt++] = i;
mu[i] = -1;
}
for (int j = 0; primes[j] * i < N; j++) {
st[primes[j] * i] = 1;
if (i % primes[j] == 0)
break;
mu[primes[j] * i] = -mu[i];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) s[i] = s[i - 1] + mu[i];
}
int g(int k, int x) { return k / (k / x); }
LL f(int a, int b, int k) {
a /= k;
b /= k;
LL res = 0;
int n = min(a, b);
for (int l = 1, r; l <= n; l = r + 1) {
r = min(n, min(g(a, l), g(b, l)));
res += (LL)(s[r] - s[l - 1]) * (a / l) * (b / l);
}
return res;
}
int main() {
init();
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
int a, b, c, d, k;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c, &d, &k);
printf("%lld\n", f(b, d, k) - f(a - 1, d, k) - f(b, c - 1, k) + f(a - 1, c - 1, k));
}
return 0;
}
T10
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=1e7+5,M=1e7;
int st[N],primes[N],cnt;
LL u[N],s[N],f[N];
LL get(int x,int y)
{
LL res=0;
for(int i=1,j;i<=x;i=j+1)
{
j=min(x/(x/i),y/(y/i));
res+=1LL*(s[j]-s[i-1])*(LL)(x/i)*(LL)(y/i);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
u[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=M;i++)
{
if(!st[i])
{
primes[++cnt]=i;
u[i]=-1;
}
for(int j=1;primes[j]<=M/i;j++)
{
st[primes[j]*i]=1;
if(i%primes[j]==0)break;
u[primes[j]*i]=-u[i];
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++)
{
for(int j=1;primes[i]*j<=M;j++)f[j*primes[i]]+=u[j];
}
for(int i=1;i<=M;i++)s[i]=s[i-1]+f[i];
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
printf("%lld\n",get(min(n,m),max(n,m)));
}
return 0;
}